What is version control?¶
- Practice of tracking and managing changes to software code.
- Keeps track of every modification.
- If a mistake is made, developers can turn back the clock.
- Each member may make their changes in several parts of the file.
- You wouldn't consider working without it even for non-software projects.
Benefits of version control¶
- A complete long-term change history of every file.
- Branching and merging.
- Traceability.
What is git?¶
- A version control system which lets you track changes you make to your files over time.
- With Git, you can revert to various states of your files (like a time traveling machine.
- Not just for source code files – you can also use it to keep track of text files or even images.
How to install git?¶
- Download the latest version on the official website.
What is GitHub?¶
- An online hosting service for Git repositories.
How to push a repository to GitHub?¶
- Create a GitHub account
- Create a repository
- Add and commit file(s)
- Push the repository to GitHub
How to add files?¶
- When we first initialized our project by
git init, the file was not being tracked by Git. - To do that, we use this command
git add . - If you want to add a specific file, maybe one named
Readme.md, you usegit add Readme.md. - Now our file is in the staged state. You will not get a response after this command, but to know what state your file is in, you can run the
git statuscommand.
How to commit files?¶
- The next state for a file after the staged state is the committed state. To commit our file, we use the
git commit -m "first commit"command. - The first part of the command
git committells Git that all the files staged are ready to be committed so it is time to take a snapshot. - The second part
-m "first commit"is the commit message.-mis shorthand for message while the text inside the parenthesis is the commit message.
How to push the repository to GitHub?¶
- Create a connection between your local repo and the remote repo on Github.
git remote add origin https://github.com/ykang/BDE2023.git
- Change your main branch's name to "main".
git branch -M main
- Push your repo from your local device to GitHub.
git push -u origin main
Creating branches¶
- Branching lets you have different versions of a repository at one time.
- By default, your repository has one branch named main.
- When you create a branch off the main branch, you're making a copy, or snapshot, of main as it was at that point in time.
- If someone else made changes to the main branch while you were working on your branch, you could pull in those updates.
Creating branches¶
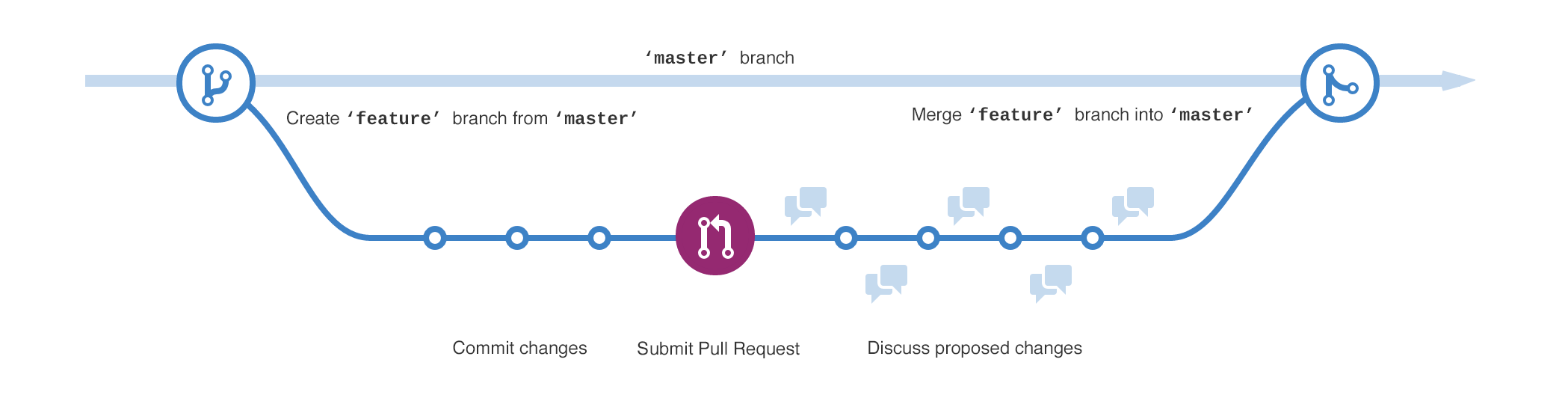
Creating new branches¶
- Now let us go to github web and create a new branch.
git branch -ato see all branches.git checkout <branch-name>to swith to another branch.
Pull request¶
- Now that you have changes in a branch off of
main, you can open a pull request. - Pull requests are the heart of collaboration on GitHub. When you open a pull request, you're proposing your changes and requesting that someone review and pull in your contribution and merge them into their branch.
Merging your pull request¶
- Merge your pull request if you agree with the changes.
Folk a repo¶
- A fork is a copy of a repository. Forking a repository allows you to freely experiment with changes without affecting the original project.
- Most commonly, forks are used to either propose changes to someone else's project or to use someone else's project as a starting point for your own idea. You can fork a repository to create a copy of the repository and make changes without affecting the upstream repository.
- For example, you can use forks to propose changes related to fixing a bug. Rather than logging an issue for a bug you've found, you can:
- Fork the repository.
- Make the fix.
- Submit a pull request to the project owner.
How to Pull a Repository in Git?¶
git clone YOUR_SSH_URL
Your turn¶
- Folk
BDE2023repo to your github. - Pull this repo to local.
- Make a directory with your full name.
- Add some files.
- Push.
- Make a pull request.
Some notes¶
- Connect to github with ssh.
- Check the git log:
git log --author="ykang" - Check the status:
git status - Check the diffs:
git diff Head~3 - Add a
.gitignorefile that specifies intentionally untracked files that Git should ignore.